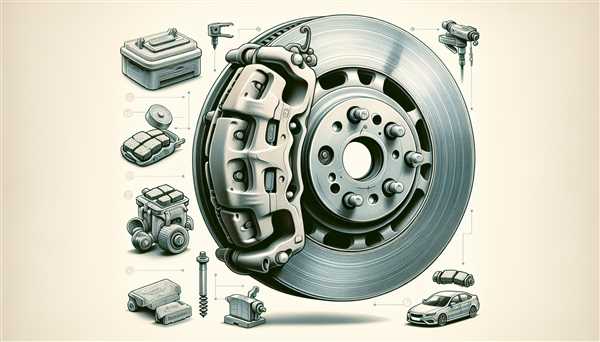
Unusual noises during braking, such as grinding or squeaking, often indicate that attention is required for the components responsible for clamping the pads against the rotors. This can signal that the hydraulic mechanism is failing, which may compromise performance.
Another critical observation is uneven wear on brake pads. If one side shows significantly more wear than the other, it could suggest that the mechanism is sticking, leading to suboptimal braking efficiency. Monitoring pad wear closely ensures timely adjustment or part updates.
Inconsistent braking performance can also be a red flag. If the vehicle pulls to one side or experiences a delay in response, this may indicate that the mechanism is not functioning correctly, affecting safety and drivability.
Fluid leakage around the wheel area is another concerning sign. The presence of brake fluid can point to a breach in the sealing mechanisms, necessitating immediate inspection and potential intervention.
Understanding Common Symptoms of Worn Brake Calipers
Unresponsive stopping action indicates a potential problem. If pressing the pedal feels soft or goes to the floor, a malfunctioning component might be at fault.
Uneven wear on the pads can signal issues with the hydraulic mechanism. Check for significant differences between the thickness of the pads on either side.
Strange sounds during braking, such as grinding or squealing, often arise from inadequate clamping force. This can lead to damage over time.
Pulling to one side when braking is an indication that force is not evenly applied. This can cause the vehicle to drift, compromising safety.
Fluid leaks around the wheels suggest a failure within the hydraulic system. Inspect for any signs of leakage, as this requires immediate attention.
Overheating components may result from excessive friction. If wheels become unusually hot, investigate the source to prevent further damage.
Steps to Inspect Your Brake Calipers for Damage
Begin by visually examining the components for signs of corrosion or fluid leaks. Look closely at the seals where the caliper meets the brake line; any signs of wetness indicate a potential seal failure.
Next, check for uneven wear on the brake pads. Discrepancies in pad thickness often suggest issues with the caliper function, prompting further inspection.
Inspect the surface of the caliper for cracks or significant wear. Any visible damage can compromise performance and may necessitate a complete overhaul of the assembly.
After visual checks, test the movement of the calipers by pressing the brake pedal. If the caliper does not retract fully, this may indicate a sticking piston, requiring further attention.
Use a dial indicator to measure the runout of the caliper bracket. Excessive movement could point to misalignment or mounting issues, affecting the caliper’s performance.
Finally, assess the hardware connections. Loose bolts or missing components can impact the integrity and safety of the entire braking system, suggesting the need for immediate action.
When to Seek Professional Help for Brake Caliper Replacement
If unusual noises, such as grinding or squeaking, occur during braking, consult a mechanic immediately. Discoloration or signs of leakage around the assembly indicate potential failures. Pay attention to uneven wear on the brake pads; this may suggest malfunctioning components that require expert assessment.
Noticeable vibration or pulling to one side while stopping can signify issues with the caliper system. If any of these symptoms appear alongside a decrease in stopping power, professional evaluation is critical. A certified technician can diagnose whether a complete overhaul of the braking system is necessary.
Regular maintenance checks should also include inspections for caliper integrity. If fluid levels drop unexpectedly or pedal feel becomes spongy, seek professional advice promptly. Addressing these issues early can prevent further damage and ensure safety on the road.










